Oxytocin: The Love Hormone or Cuddle hormone.
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide known for its pivotal role in social bonding, reproduction, and emotional regulation, often referred to as the “love hormone” or “cuddle hormone.” Here’s a detailed explanation of oxytocin:
Chemical Nature
- Structure: Oxytocin is composed of nine amino acids, making it a nonapeptide. It has the chemical formula C43H66N12O12S2.
- Production: It is synthesized in the hypothalamus, a region of the brain, and stored and released by the posterior pituitary gland into the bloodstream. It consists of nine amino acids and plays essential roles in various physiological and behavioral processes.
What Does Oxytocin Do?

- Social Bonding:
- Enhanced Social Interactions: Oxytocin fosters feelings of trust, empathy, and bonding between individuals, crucial for nurturing relationships.
- Pair Bonding: It strengthens romantic attachments and facilitates parental bonding with infants.
- Reproductive Functions:
- Labor and Delivery: Oxytocin triggers uterine contractions during childbirth, aiding in labor progression.
- Breastfeeding: It stimulates milk ejection reflex (let-down), ensuring adequate milk flow during nursing.
- Emotional Regulation:
- Stress Reduction: Oxytocin lowers cortisol levels, promoting relaxation and reducing stress and anxiety.
- Mood Enhancement: It contributes to feelings of happiness and well-being, enhancing overall mood.
- Sexual Activity:
- Intimacy: Oxytocin levels surge during sexual arousal and orgasm, facilitating emotional closeness between partners.
- Behavioral Effects:
- Maternal Behaviors: Oxytocin promotes maternal instincts and nurturance towards offspring.
- Social Behaviors: It encourages prosocial behaviors like cooperation, generosity, and altruism.
How Can Oxytocin Affect Mental Health?

- Stress and Anxiety Reduction:
- Calming Effect: By dampening the stress response and reducing cortisol, oxytocin promotes a sense of calm and relaxation.
- Social Support: It enhances the buffering effects of social support systems, improving resilience to stress.
- Depression:
- Mood Improvement: Oxytocin’s antidepressant-like effects may alleviate symptoms of depression and enhance emotional well-being.
- Social Connection: Increased oxytocin levels foster social connections, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Anxiety Disorders:
- Social Anxiety: Oxytocin can alleviate social anxiety by enhancing social skills and reducing fear responses in social situations.
- Generalized Anxiety: It has anxiolytic properties, helping to manage symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
- Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD):
- Social Skills: Studies suggest oxytocin improves social interactions and communication skills in individuals with ASD.
- Behavioral Regulation: It may reduce repetitive behaviors and enhance emotional recognition.
- PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder):
- Stress Response: Oxytocin modulates the stress response, potentially mitigating symptoms of PTSD and improving coping mechanisms.
- Emotional Healing: Enhanced social bonding and support may aid in emotional recovery from trauma.
- Interpersonal Relationships:
- Trust and Empathy: Increased oxytocin levels promote trust, empathy, and bonding in interpersonal relationships.
- Conflict Resolution: It improves conflict resolution skills and reduces aggression, fostering healthier relationship dynamics.
How Are Oxytocin Levels Controlled?
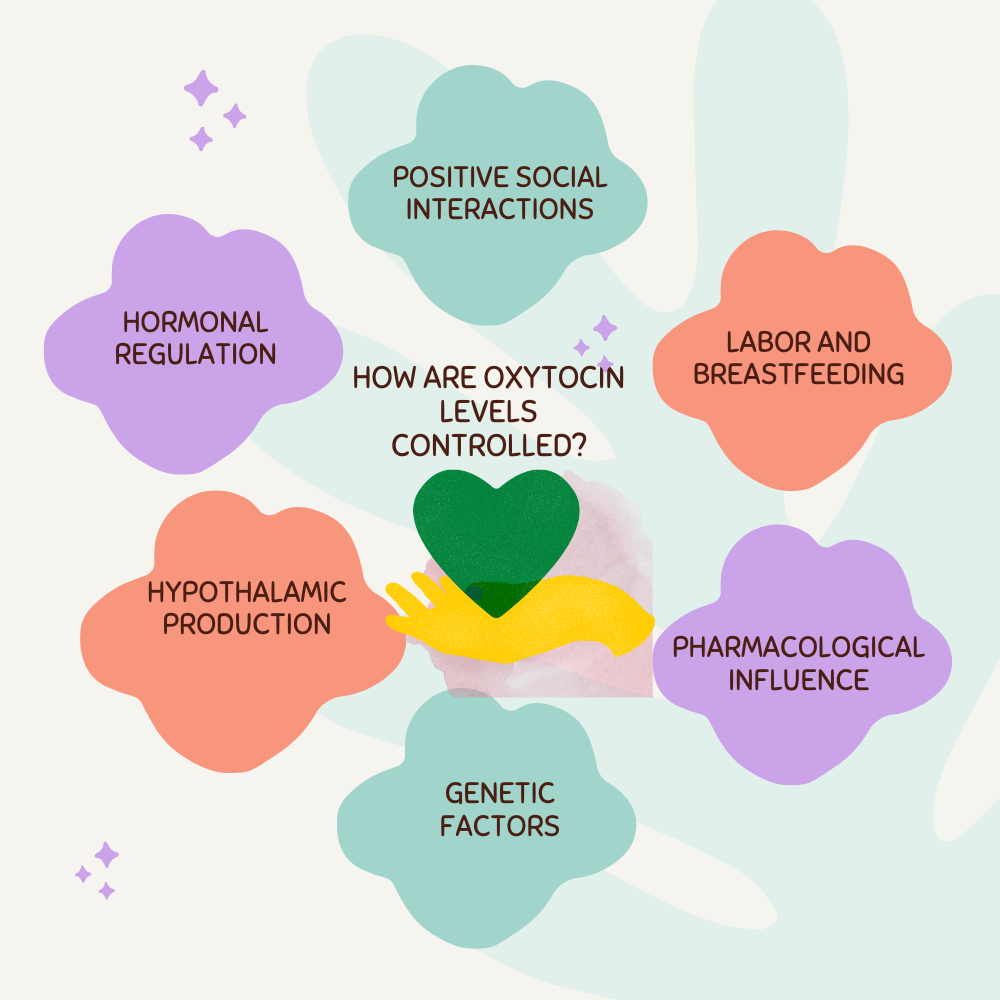
- Neural Control:
- Hypothalamic Production: Oxytocin is synthesized in the hypothalamus and released into the bloodstream via the posterior pituitary gland.
- Stimulus-Driven Release: Neural signals triggered by sensory stimuli, emotional cues, and physical touch can stimulate oxytocin release.
- Hormonal Regulation:
- Positive Feedback: During childbirth and breastfeeding, oxytocin release operates on a positive feedback loop, reinforcing its own production.
- Autoregulation: Oxytocin can regulate its release through feedback mechanisms involving its receptors.
- Environmental and Behavioral Factors:
- Social Interaction: Positive social interactions, nurturing behaviors, and physical affection increase oxytocin levels.
- Stress Reduction: Relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, and massage promote oxytocin release.
- Physiological Triggers:
- Labor and Breastfeeding: Uterine contractions during labor and suckling by infants trigger oxytocin release, facilitating childbirth and breastfeeding.
- Pharmacological Influence:
- Synthetic Oxytocin: Medicinally administered (e.g., Pitocin) to induce labor, manage postpartum bleeding, and in some therapeutic contexts.
- Substance Effects: Certain substances (e.g., MDMA) temporarily increase oxytocin levels, though not recommended due to associated risks.
- Genetic Factors:
- Oxytocin Receptor Genes: Genetic variability in oxytocin receptor genes influences individual responses to oxytocin, affecting social behaviors and emotional responses.
How to Increase Oxytocin ?
To naturally elevate oxytocin levels:
- Engage in physical touch and affectionate gestures such as hugging, cuddling, and holding hands.
- Foster positive social interactions by spending quality time with loved ones and expressing kindness.
- Participate in group activities and community engagements that promote social bonding and support.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and massage therapy.
- Engage in sexual activity, particularly intimate moments that promote emotional closeness.
- Support breastfeeding for mothers, as suckling stimulates oxytocin release and supports maternal bonding.
- Create a nurturing and supportive environment at home and work, emphasizing trust, empathy, and positive communication.
FAQs about oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone” or “cuddle hormone”:
- What is oxytocin?
- Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland. It plays a crucial role in social bonding, reproduction, and emotional regulation.
- How does oxytocin influence social bonding?
- Oxytocin enhances feelings of trust, empathy, and closeness between individuals, promoting social connections and emotional bonding.
- What are the physiological functions of oxytocin?
- Oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and facilitates milk ejection during breastfeeding. It also influences emotional responses and stress regulation.
- What are the effects of oxytocin on mental health?
- Oxytocin can reduce stress and anxiety by lowering cortisol levels and promoting relaxation. It may also improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression, and enhance emotional well-being.
- How is oxytocin released?
- Oxytocin is released in response to various stimuli, including physical touch, positive social interactions, and emotional cues. It operates on feedback loops during childbirth and breastfeeding.
- Can oxytocin be used therapeutically?
- Synthetic oxytocin (Pitocin) is used medically to induce labor, control postpartum bleeding, and in some cases, for therapeutic purposes in psychiatric disorders like autism and PTSD.
- What natural activities increase oxytocin levels?
- Engaging in physical affection such as hugging, cuddling, and holding hands boosts oxytocin. Positive social interactions, mindfulness practices like meditation, and regular exercise also help.
- How does oxytocin affect relationships?
- Oxytocin promotes trust, cooperation, and emotional intimacy in relationships. It can enhance communication, reduce conflict, and strengthen bonds between partners and within families.
- Are there risks or side effects associated with oxytocin?
- While generally well-tolerated, excessive oxytocin release or administration can lead to uterine hyperstimulation during labor or allergic reactions. Synthetic oxytocin should be used under medical supervision.
- What role does oxytocin play in maternal and paternal bonding?
- Oxytocin is crucial for maternal bonding with infants, fostering nurturing behaviors and attachment. It also plays a role in paternal bonding and caregiving behaviors.